Welcome to Real Health and Fitness
Our blog features expert content covering topics like Nutrition Consulting and Personal Training, Healthy Recipes, and the latest in Supplements and Health Trends.
Subscribe to GET new journal





Your journey to a healthier, more vibrant life starts here!
Transform Your Health with Personalized Nutrition & Fitness Plans
At Real Health and Fitness, we’re dedicated to providing trusted insights, expert tips, and personalized guidance on nutrition, fitness, and overall well-being. Whether you’re looking to transform your diet, achieve fitness goals, explore supplements, or simply find delicious, healthy recipes, our site offers the tools and knowledge you need to succeed.
Nutrition Consulting and Personal Training
Our personalized nutrition consulting service provides expert guidance to help you make smarter food choices and build a balanced diet that suits your unique lifestyle and health goals. Whether you’re looking to improve energy levels, manage weight, or optimize your overall health, our nutrition experts are here to help.
Customized Meal Plans
Tailored meal plans that fit your goals, dietary needs, and lifestyle.
Workout Plans
Workouts that cater to your fitness level, goals, and body type.
Flexible Training
Options for in-person or online sessions to fit your schedule.
Supplements and Health
Our personalized nutrition consulting service provides expert guidance to help you make smarter food choices and build a balanced diet that suits your unique lifestyle and health goals. Whether you’re looking to improve energy levels, manage weight, or optimize your overall health, our nutrition experts are here to help.
Recommendations
Tailored advice based on your health goals and dietary needs.
Quality & Safety
Guidance on choosing high-quality, trusted supplement brands.
Re-Evaluation
Ongoing assessments to adjust supplement intake as your health evolves.
Healthy Recipes
Enjoying nutritious, delicious meals is key to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Our healthy recipe development service offers creative, easy-to-follow recipes that align with your nutritional goals while keeping meals exciting and enjoyable.
Nutritious & Delicious
Recipes that prioritize both health and taste.
Catering to Dietary
Options for vegan, gluten-free, and other dietary needs.
Seasonal
Recipes that use accessible ingredients without compromising on quality.
What People Are Saying
Health & Fitness Updates
Subscribe to receive the latest in nutrition, fitness, and healthy living. Get expert tips, recipes, and wellness insights delivered directly to your inbox as soon as they’re available at realhealthandfitness.com.
Latest Articles

10 Effective Workouts for Busy Professionals
Get maximum impact from your workouts even with a busy schedule with these 10 effective routines: HIIT workout, German Volume Training, full-body movements, stationary bike, rowing machine, dumbbell exercises, resistance bands, calisthenics, kickboxing, and circuit training.
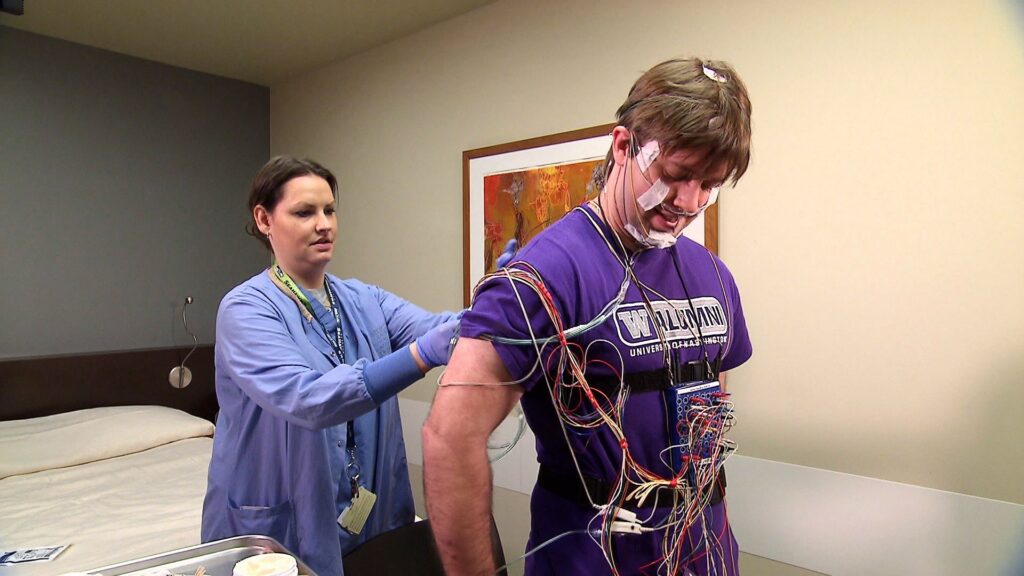
A Guide to Home Sleep Testing for Better Health
Sleep is a fundamental aspect of our overall well-being, and when we experience disruptions in sleep, the impact on our health can be profound. For many, diagnosing sleep-related issues often begins with specialized testing, including sleep studies.
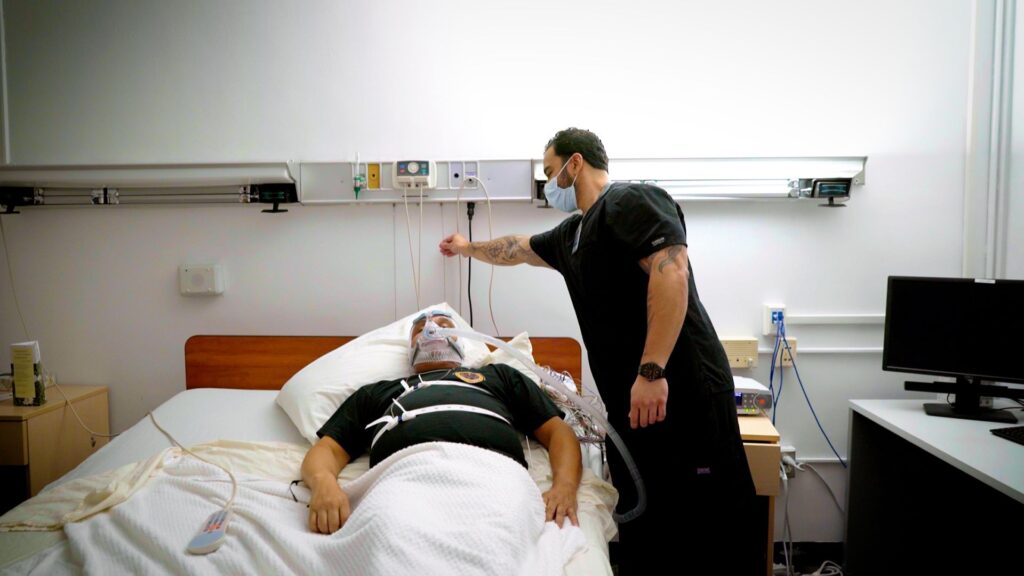
Top Sleep Disorder Tests to Diagnose and Treat Your Sleep Issues
Struggling with sleep can be incredibly frustrating and disruptive to daily life. Fortunately, advancements in medical science offer effective sleep disorders tests that can help diagnose and treat various sleep conditions.
